PowerTable: Microsoft Fabric's Missing Business Application Workload
Microsoft Fabric aims to unify everything from data integration and engineering to batch and real-time analytics under a single, cohesive SaaS data platform. Beyond analytics, the platform has also branched out into transactional use cases with the likes of SQL databases or Activator event detections.
But that still leaves many operational scenarios that require bulk data editing, commenting, or user-facing automations. How do you empower business users to interact with, update, and enrich the data in Fabric without compromising the entire architectural vision?
This interactive business application layer is a significant gap often addressed through suboptimal options:
- Commission Custom Development: A slow, expensive, and resource-intensive path that creates a new application to maintain, secure, and update, adding to an already long development backlog. We’re talking about read-write production business applications here, not the low-stakes prototypes or lightweight websites that you could reasonably expect a business user to vibe code with AI.
The same workload development kit we at Lumel use to create our Fabric workload is available to companies that want to create in-house Fabric apps, but it definitely isn't a no-code experience!
- Use External Low-Code Platforms: Tools like Power Apps are powerful but are not native Fabric workloads. They often involve extra data movement and storage, which can introduce extra latency, complexity, or costs, and often violates the "single source of truth" principle of OneLake.
For reference, we explain in detail at the end of this entry how Dataverse, the database that powers Power Apps and Dynamics 365, integrates with Fabric through a range of patterns that fall short of seamless bidirectional read/write support. In any case, Power Apps and PowerTable cover very different use cases and can be made to work together with a bit of (Fabric-based) orchestration.
- Limp Along Using Spreadsheet Workarounds: The path of least resistance, but one that completely breaks the governance, security, and real-time value of Fabric the moment data is (un)managed in spreadsheets. Excel workbooks are limited to one million rows, and while workarounds exist, they're brittle and high maintenance.
In the end, these options force a compromise: sacrifice speed, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, or governance. Of course, any solution is going to involve tradeoffs, but there is a fourth option that alleviates many of the issues we just reviewed.
1. PowerTable: Editing Data in Place, Responsibly and At Scale
We designed PowerTable from the ground up to be the missing workload for business applications in Microsoft Fabric. It is not an external tool integrated with Fabric; it is a Fabric-native workload that runs directly in it, right next to your data, vastly simplifying the end-to-end architecture and maximizing the return on existing investments.
Here is how PowerTable fills the data application gap:
- A user experience familiar to Power BI/Fabric users and admins: PowerTable complements Fabric's underlying infrastructure for compute, security, and governance, and its user interface puts it one click away from familiar experiences such as Power BI reports. User authentication is managed through Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), and access is determined by the permissions already established in Fabric workspaces.
- Support for OLAP, OLTP, and hybrid scenarios: PowerTable is built to handle both analytical processing (OLAP) and the transactional capabilities (OLTP) required to underpin business applications, thanks to its ability to read from Fabric but also competing lakehouses and warehouses (Snowflake, Databricks et. al.), SQL Server, as well as write back to Azure/Fabric SQL. The ability to read from Power BI semantic models adds an interesting twist that we’ll cover in depth in a future entry.
- Pushdown SQL with No Data Replication: This is our core architectural advantage. PowerTable does not have its own database and never replicates your data. All interactions—reads, writes, updates, and deletes—are translated into SQL statements and pushed down to be executed directly in the database sink of your choice. This zero-replication model means there is no data movement, no Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) process to manage, no additional storage costs, and zero latency between the user's action and the update to your existing single source of truth.
2. From Technical Advantage to Business Velocity
For a Fabric Architect or IT Director, this architectural consistency delivers compelling benefits:
- Eliminate Technical Debt: By avoiding data replication and complex integrations, you prevent the creation of brittle data pipelines and siloed data stores that will need to be maintained in the future.
- Accelerate Time-to-Value: Empower business analysts and power users to build the apps they need in hours, not months. This clears your development backlog and makes your business more agile.
- Guarantee Governance and Control: Maintain a single, auditable, and secure environment for all data interaction, ensuring that user-driven applications adhere to the same stringent standards as your core data platform.
- Maximize Fabric ROI: Drive deeper adoption and unlock new use cases for your Fabric investment by giving users the tools they need to not only analyze data but to act on it safely and efficiently.
3. Next Step: Schedule an Architectural Deep-Dive
Fabric is a very versatile tool that offers several options for most jobs. What it doesn’t offer at all is a user-friendly, grid-based tool to add accessible, no-code data entry to your data projects. Request a 30-minute overview with our team to see a live demonstration of our pushdown SQL processing in action and review your architectural considerations and answer any questions you might have.
4. Annex: Understanding Microsoft's Current Dataverse-Fabric Integration Patterns
To provide complete context for the business application gap discussed above, it's important to understand Microsoft's current integration approaches between Dataverse and Fabric. As always, Microsoft offers a variety of paths to achieve the same high-level goal, each one a better fit for specific use cases or user personas, and each coming with its own architectural implications, limitations, and considerations.
We aim to provide a fair and objective assessment here, so remember that Power Apps and the Common Data Service (CDS – Dataverse’s initial name) where launched in 2016, years before Fabric. There are good historical reasons that explain the current range of integration options.
Data app platforms outside of the Microsoft ecosystem will fall into some variation of Pattern 5, which involves at least one layer of user-managed ETL, in or outside Fabric (e.g., using Azure Data Factory or Fivetran). We will cover this in detail in future entries.
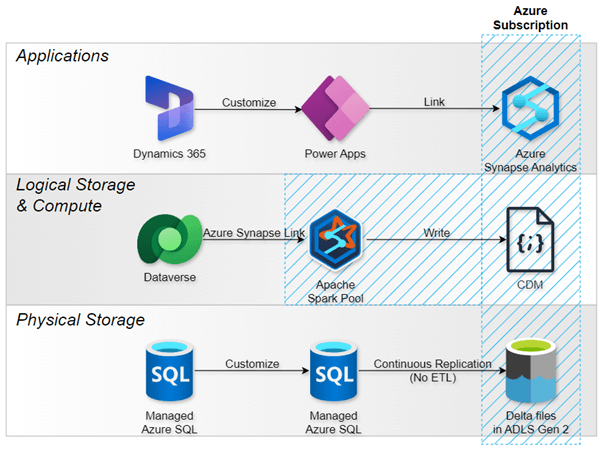
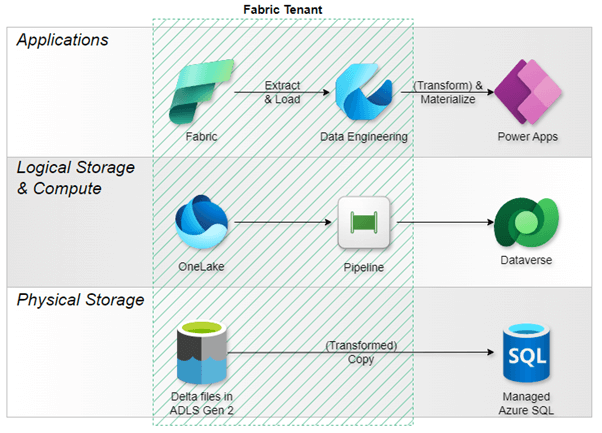
5. Pattern 1: Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse (Legacy)
Direction: Dataverse → Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (ADLS Gen2) + Azure Synapse Analytics
Architecture: Data export/replication to customer-owned Azure resources
Use Case: Enterprise analytics requiring dedicated Azure infrastructure
Source: What is Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse? (06/20/2022)
Summary: This is the evolution of the original "Export to data lake" feature, renamed in 2021. Organizations provision their own Azure storage and Synapse workspaces, giving them full control over compute and storage costs but requiring additional infrastructure management.
Note that you can “link your existing Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse profiles with Fabric from the Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse area. You need to select the Enable Parquet/Delta lake option to enable the view in the Fabric feature for Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse profiles.” Caveat: this is not available for Dataverse profiles that use CSV output.
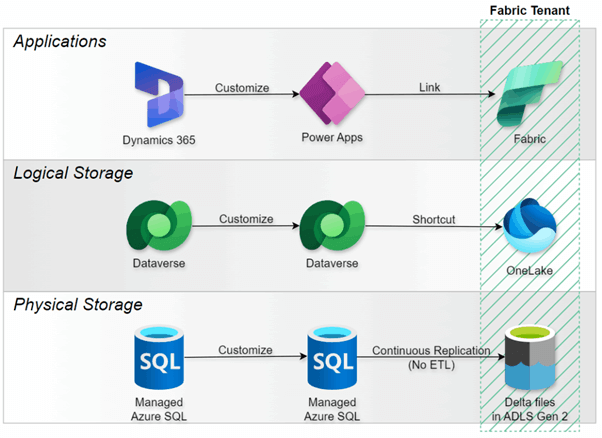
6. Pattern 2: Link to Microsoft Fabric
Direction: Dataverse → OneLake
Architecture: Direct shortcuts with no data copying activity
Use Case: Simplified analytics integration without separate Azure resources
Source: Link your Dataverse environment to Microsoft Fabric and unlock deep insights (05/13/2025)
Summary: Microsoft's modern approach creates shortcuts from Dataverse directly into OneLake using delta format. This eliminates data duplication work and simplifies management by leveraging Dataverse's built-in (virtual) storage.
This is how Microsoft compares the two approaches:
| Link to Fabric | Azure Synapse Link |
|---|---|
| No copy, no ETL direct integration with Microsoft Fabric. | Export data to your own storage account and integrate with Synapse, Microsoft Fabric, and other tools. |
| Data stays in Dataverse - users get secure access in Microsoft Fabric. | Data stays in your own storage. You manage access to users. |
| All tables chosen by default. | System administrators can choose required tables. |
| Consumes additional Dataverse storage. | Consumes your own storage as well as other compute and integration tools. |
Let’s parse what this means: you do not have to manage a copy activity or ETL process, but behind the scenes, there is actually a replica of your Dataverse data generated for you in OneLake. In other words, you don’t have to actively “copy” as a verb, but there is a “copy” (as a noun) generated for you.
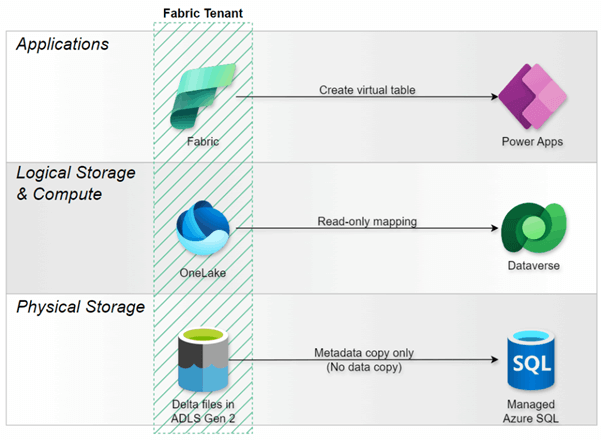
7. Pattern 3: Virtual Tables from Fabric
Direction: OneLake → Dataverse
Architecture: Read-only virtual tables sourced from Fabric lakehouses
Use Case: Building Power Apps with Fabric-stored data
Source: Build apps and automations, drive action with insights from Microsoft Fabric (03/10/2025)
Summary: this pattern enables low-code application development using data that resides in Fabric, but with a critical limitation: virtual tables are explicitly read-only. Microsoft's documentation states that "you can't modify the data in Fabric OneLake with Power Apps."
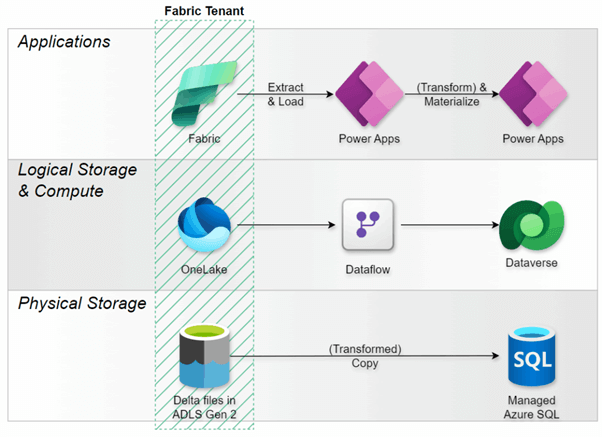
8. Pattern 4: Low-Code ETL with Power Apps Dataflows
Direction: Fabric Lakehouse → Dataverse
Architecture: Extract/Load from OneLake’s DFS endpoint, optionally Transform, then write to new or existing Dataverse tables
Use Cases: “Reverse ETL” from Fabric back into operational systems, such as data enrichment (e.g. bringing ML-scored data) or periodic aggregations
Source: Power Query - Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (02/22/2024)
Summary: Dataflows in Power Apps use the same familiar Power Query interface found in Power BI and Fabric, so this is a viable option. However, it requires jumping back and forth between Power Apps and Fabric. Bulk edits would in many cases require heavy lifting in Power Query / M compared with PowerTable’s no code user interface. And several use cases core to PowerTable such as cell-level commenting are outright out of Power Query’s scope.
9. Pattern 5: Low-Code ETL with Fabric Pipelines
Direction: Fabric Lakehouse → Dataverse
Architecture: Copy activity lakehouse files or tables via Fabric pipeline into Dataverse tables
Use Cases: same as Pattern 4
Summary: if you just want to copy data from Fabric to Dataverse without transforming it (i.e., EL pattern with T), this is likely your most straighforward and efficient pattern. Like with pattern 4, it puts you in the business of copying data between two platforms.
If you intend to create a hybrid solution that combines Fabric, PowerTable, and Dataverse, explore this pattern first. We'll provide reference architectures for this type of project in a future post.
10. Architectural Reality Check
While these patterns can work together to create quasi-bidirectional flows, there is no native, fully bidirectional integration between Dataverse and Fabric. Pattern 2 flows data from operational systems to analytics, while Pattern 3 surfaces analytical data for read-only consumption in applications, and Pattern 4/5 add a layer of EL/ETL and orchestration.
For scenarios requiring true bidirectional interaction—where business users need to update, enrich, or transact against Fabric data—organizations currently face the architectural compromises outlined in the main article: custom development, external platforms with data replication, or governance-breaking spreadsheet exports.
Microsoft's integration patterns excel at their intended purposes: moving operational data to analytics (Pattern 2) and surfacing analytical insights in low-code applications (Pattern 3). However, the interactive business application layer that enables no-ETL, governed, transactional interaction directly with Fabric data remains an architectural gap in the current Microsoft stack that PowerTable aims to address.
This assessment reflects Microsoft's published capabilities and limitations. based on Microsoft Learn documentation current as of August 2025.